Discovery service
NHS Knowledge and Library HubHow users discover content using the Hub.
EBSCO Discovery Service (EDS)
The user front-end of the NHS Knowledge and Library Hub is powered by EDS.
It includes a powerful, semantic search plus advanced and PICO search options.
A search of the NHS Knowledge and Library Hub retrieves results from EBSCO’s Knowledge Base which has been tailored to meet the needs of NHS staff and learners.
The default setting is for Guest searching but users are directed to sign in using their NHS Open Athens account.
Logged in users will:
- have full access to licenced content, folders for saving results to and export options
- if they receive a full library service, be able to request documents and, if it’s set up locally, use Ask-a-Librarian
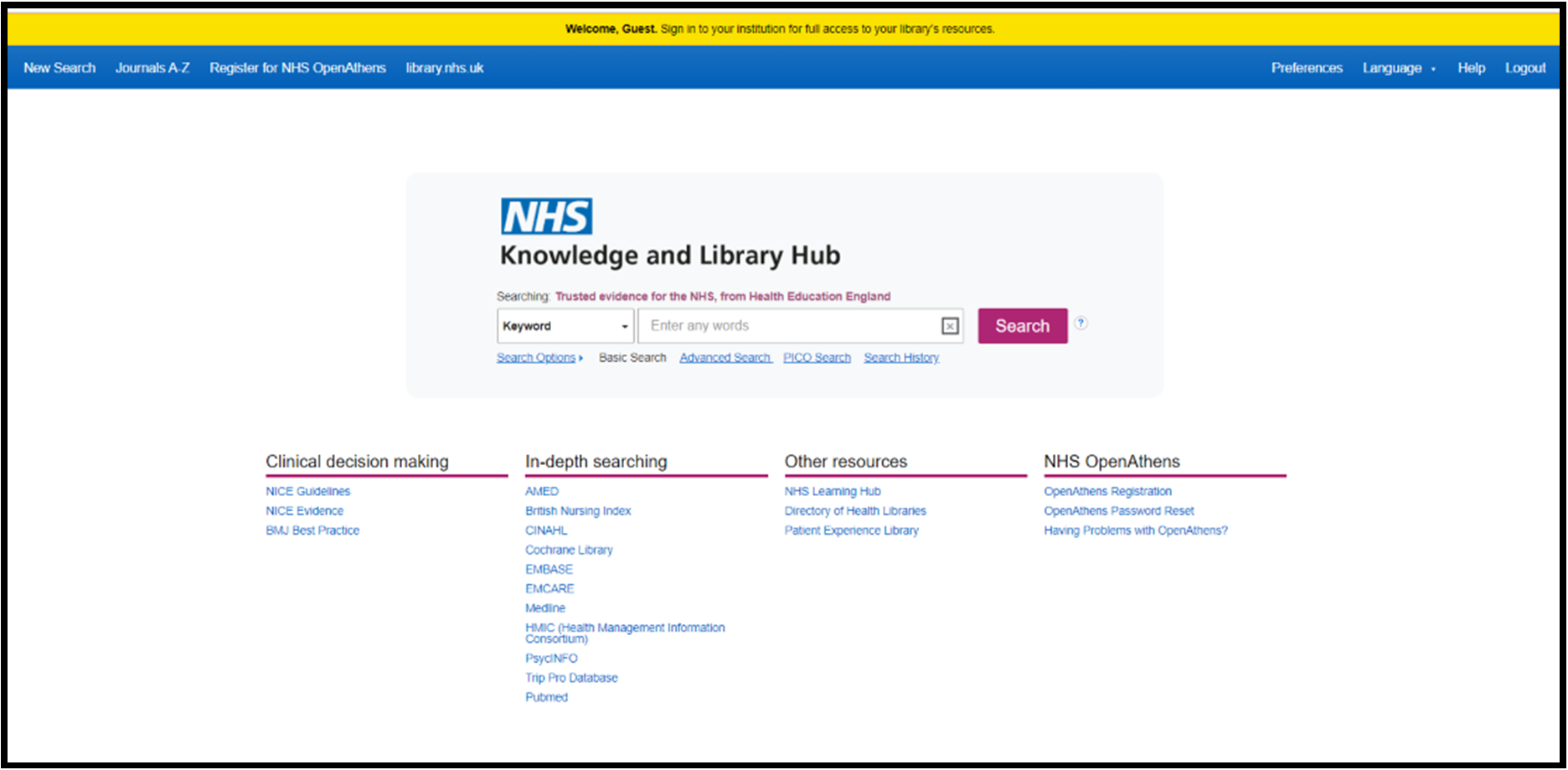
Search the NHS Knowledge and Library Hub. Log on using your NHS OpenAthens account for access to full text content and local knowledge and library services.
Promotional links are available (listed on this FAQ) that direct users onto your local version of the Hub. This allows them to see the correct content and local links before they login.
If you have any comments or feedback, send them to the Knowledge for Healthcare team on [email protected].
Is the NHS Knowledge and Library Hub single-sign-on?
Yes, OpenAthens is the primary authentication method.
We are working with NICE, JISC and suppliers to improve the authentication and platform account experience for all interfaces, including the NHS Knowledge and Library Hub.
What resources are searchable through the NHS Knowledge and Library Hub?
All nationally-funded subscription resources (including National Core Content databases and journal collections, BMJ Best Practice, the Royal Marsden Manual, Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry, Oxford Medical Textbooks and Handbooks, and the Cochrane Library).
Selected open access and repository collections.
All locally-funded subscription journals.
An increasing number of library collections via integrated library management systems.
EBSCO work with other suppliers to make wide range of resources discoverable and we are working with them to expand the range.
How do all the components link up?
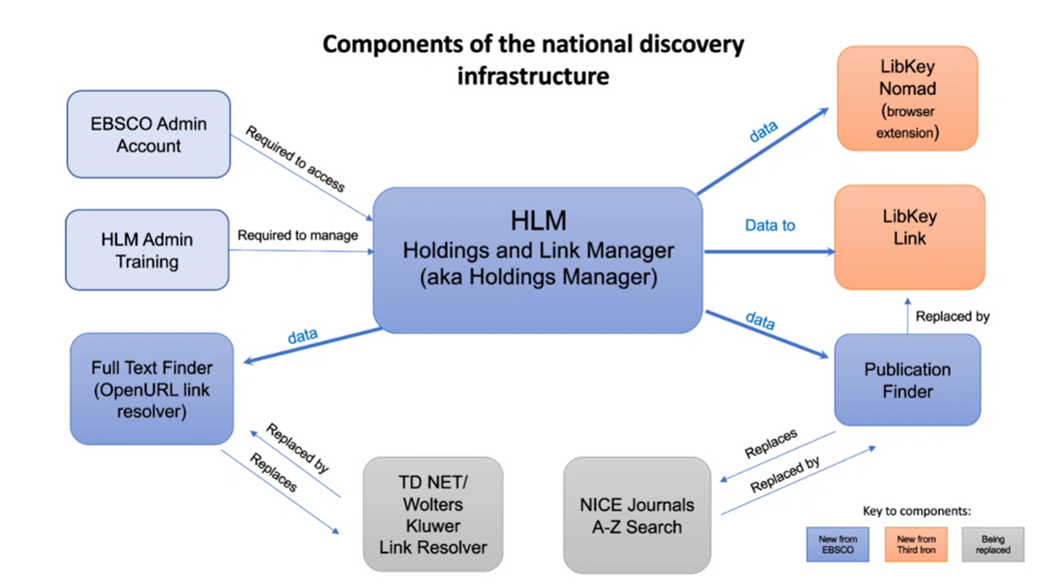
EBSCO holdings link manager (HLM) connects to the Full Text finder, EBSCO's link resolver and to LibKey Link and LibKey Nomad.
Wolters Kluwer's link resolver, currently used for My Journals and HDAS was retired in March 2022.
Can I change the widgets to include content we buy locally?
Widgets allow you to link across to other resources and interfaces such as databases via Ovid or Proquest.
All instances are set up with the national widgets.
Widgets for other commonly used resources were also added as part of the set up.
You can request additional widgets where you have the resource and one is available. See the full list and contact the Service Desk.
What if users are overwhelmed by the number of results? Won’t this end up being a glorified Google?
No. The system is designed to reproduce some of the ease and intuitiveness of Google-style searching because we know that staff and learners want the service to match Google’s convenience.
But the NHS Knowledge and Library Hub searches carefully selected sources in EBSCO’s Knowledge Base tailored to the needs of NHS staff and leaners. It includes paid for resources not visible through Google searches and has seamless linking enabled by LibKey.
The NHS Knowledge and Library Hub also allows the user to filter results in ways that Google doesn’t.
How will document requesting work?
If a digital version of an item is not available, the user will see a Request button instead.
Clicking request will open an email, pre-populated with the item’s citation details and your library’s document supply request email address.
Your library will receive the request by email to be processed in the normal way.
Will users think that the NHS Knowledge and Library Hub replaces expert searches?
We know from libraries that already use Discovery that the bulk of users will be self-sufficient in their day-to-day, basic searches.
The experience of searching the Hub is very different to an expert search and users have different expectations based around speed and convenience.
Introducing your users to the Hub can be a positive way to explain when they should work more closely with you on an expert search.
Users are already carrying out numerous searches away from expert tools and the Hub offers a better place for them to carry these out.
If users can also carry out simple searches on the Hub this should free up time for knowledge specialists to deliver expert search services.
Expert searches are required for patient care, guideline and service development, research and systematic review with the Hub unsuitable for precision searching.
The NHS Knowledge and Library Hub links users to their library services for additional support through the “Ask a librarian” link.
What training do end-users need on the NHS Knowledge and Library Hub?
Prior to the launch of the Hub librarians who already had a Discovery system indicated that many users are self-sufficient with basic searching on Discovery.
Experience subsequently has been that users benefit from a brief demonstration of the system, for example at induction, or pointers at the enquiry desk.
Inclusion of the Hub as part of wider training sessions helps users gain the initial awareness that helps them get started.
Research in 2023 demonstrated that users value tips on the key features of the Hub – the benefit of logging in early in their session, simple search tips, how to filter and the path to reading the article or other material they find. An editable slide deck has been created that can be modified as required in support of user training.
NHSE is providing ongoing marketing and communication support to help you engage with your end-users.
Details are provided via the Resource Discovery Digest and materials can be found on the Future.nhs.uk platform in the NHS Knowledge for Healthcare promotional resources space.
Page last reviewed: 30 April 2024